In materials science, complex relationships exist between the properties of materials and their composition and processing. For this reason, digital transformation in this domain presents a particularly great challenge.
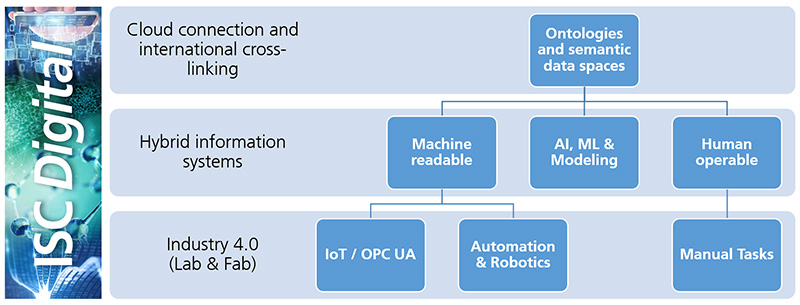
At Fraunhofer ISC, we are facing this challenge with a broad-based strategy that closely links work at all relevant levels. In this context, we have set ourselves the goal of developing toward Lab 4.0, documenting scientific processes in a central information system in a way that can be read by machines, and standardizing data structures in accordance with international standards.
Developing better materials faster: Materials Acceleration Platforms (MAPs)
At ISC, there are already several MAPs projects on different materials and related processes. We not only develop the appropriate IT infrastructure but also develop the robotic hardware. We are glad to advise companies on the first steps in this new innovative field.