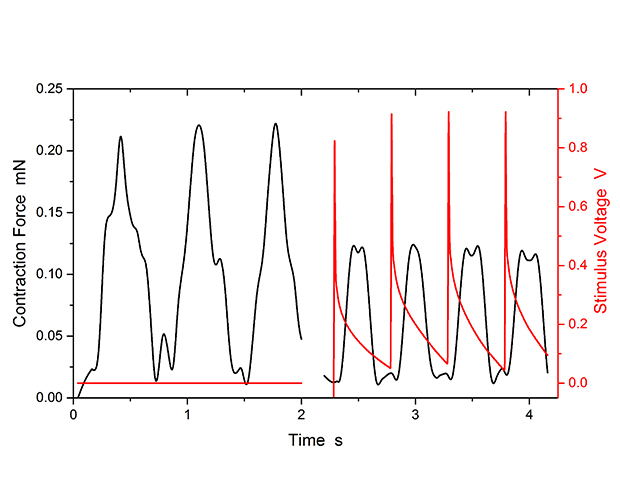
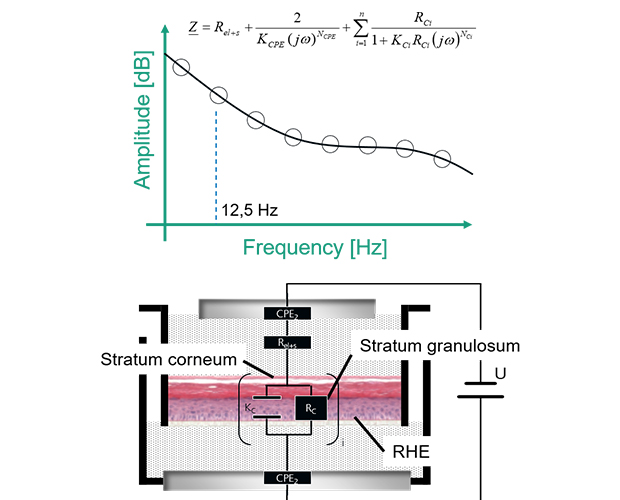
We analyze ex vivo tissue or in vitro tissue models using both invasive and non-invasive methods.
This includes, for example, pharmacological stimulation in an organ bath or measurements of the (complex) transepithelial / transendothelial resistance. We perform (immuno)histochemical work-up of fixed and embedded tissue samples and subsequently analyze them using microscopy techniques.